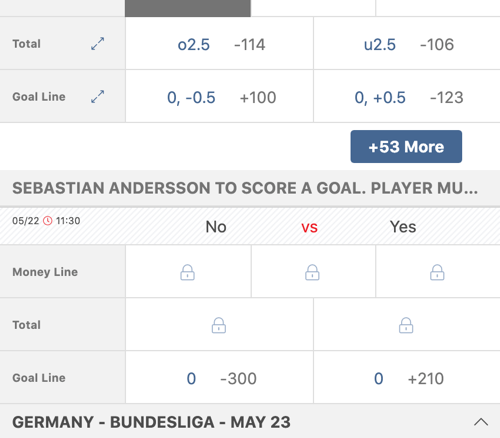
BetCRIS Sportsbook – Online Sportsbook
Casino And Slots
Welcome to the Best Casino & Slots Reviews in for 2025!
The world of casinos is constantly evolving, and in 2024, Global players have more options than ever before. Our website is designed to help you find the best and most reliable online casinos in Finland, so you can enjoy a safe and entertaining gaming experience.

Casino And Slots
Casino And Slots

Casino And Slots

Casino And Slots

Casino And Slots
Why Trust Our Casino Reviews?
We provide you with honest and expert reviews of the most popular online Casinos & Sports book.
Our team consists of experienced players and casino industry experts who thoroughly test each casino. Our reviews focus on the most important features of casinos, such as bonuses, game selection, payment methods, customer service, and security.
This ensures that you have all the necessary information before deciding where to play.

Innskuddsbonus casino

Nye casino no deposit bonus

Casino And Slots

Casino And Slots
Casino And Slots
Updated Reviews for 2025
We ensure that our reviews are always up to date. The year 2025 brings new casinos, new games, and exciting bonus offers. We closely monitor market developments and regularly update our reviews so that you can always play at the best and most reliable casinos.
The Best Bonuses and Offers for Finnish Players
One of the biggest reasons why players choose a particular casino is the bonuses it offers. Our site provides comprehensive information about the best bonuses of 2024, including welcome bonuses, free spins, and VIP programs. Our reviews help you find the casinos offering the best promotions for all players.
Safety and Reliability First
When you choose an online casino based on our recommendations, you can be confident that all the casinos we review are fully licensed and safe. We check that the casinos have the appropriate licenses for players and that their payment methods are reliable and fast.
Find the Best Casino Today!
Whether you’re a new player or an experienced veteran, our website makes it easy to find the best online casinos for 2025. Explore our reviews, choose the casino that suits you, and start playing safely and enjoyably!
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
